On This page |
On Related Pages |
|
See instructions for General Sage AWS accounts.
Use your individual AWS account under the Sage consolidated bill for AWS experiments. The rule of thumb is that if you cannot shut off what ever you are running while you are on vacation, it belongs in the Production AWS Account.
Use the platform@sagebase.org account for:
You can also use your IAM account if you like but many AWS services do not support it yet such as Beanstalk. There is a different link to log into the AWS console with your IAM login and password: https://325565585839.signin.aws.amazon.com/console/ec2
You can find them on our shared servers. When storing passwords locally on your laptop (which already has an encrypted drive, yay!) you might also consider using Password Safe.
/work/platform>hostname sodo /work/platform/PasswordsAndCredentials>ls AtlassianAccountAWSCredentials platformStagingEncryptionKey.txt crowdServerCertificate SshCertificates passwords.txt SshKeys PlatformAWSCredentials StackCredentials PlatformIAMCreds wildcard-sagebase.org-cert platformPropertyEncryptionKey.txt |
ssh -i PlatformKeyPairEast.pem ec2-user@<the ec2 host>
For screen shots see EC2 docs
For screen shots see EC2 docs
Window's users can also connect using PuTTY or WinSCP, however you will to first create a PuTTY private key file using puttygen.exe
Here is how to create the private key file:
Once you have a PuTTY private key file you can use it to connect to your host using PuTTY or WinSCP.
To connect with WinSCP:
AWS occasionally has issues. To figure out whether the problem you are currently experiencing is their fault or not:
If you use EBS-backed AMIs you can "stop" (not "terminate") your instance when you are not using it. Your root partition and other EBS volumes stick around and you are only charged for EBS usage while the instance is "stopped". When you need to use it again you "start" the instance and then re-start your applications.
You can also start with a less expensive instance type easily upgrade to a larger size in this same manner. One thing to note is that you cannot switch between 32bit to 64bit OS - choose well for your initial choice.
We enforce HTTPS-only access to S3 for all buckets. The bucket policies can be found here: http://sagebionetworks.jira.com/source/browse/PLFM/trunk/configuration/s3Policies
Use Elastic MapReduce to run a script on all our logs in the bucket logs.sagebase.org. There are some scripts in bucket emr.sagebase.org/scripts that will do the trick. If you want to change what they do, feel free to make new scripts.
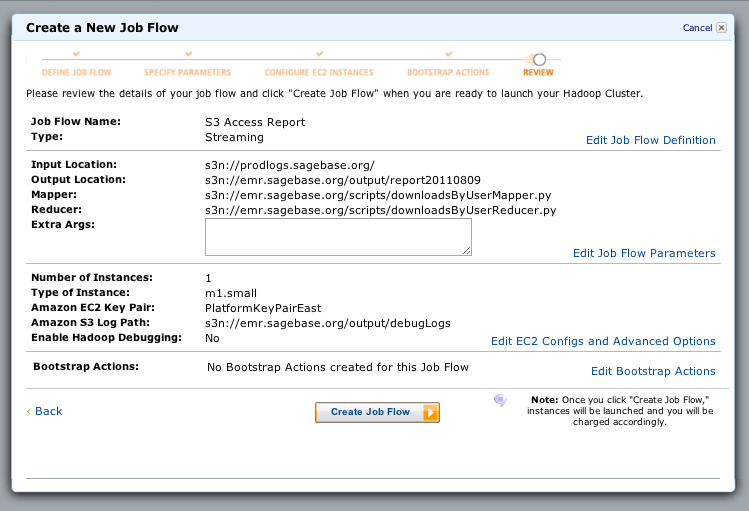
Here is what a configured job looks like:
for the purpose of cutting-and-pasting:
Input Location: s3n://prodlogs.sagebase.org/
Output Location: s3n://emr.sagebase.org/output/report20110809
Mapper: s3n://emr.sagebase.org/scripts/downloadsByUserMapper.py
Reducer: s3n://emr.sagebase.org/scripts/downloadsByUserReducer.py
Amazon S3 Log Path: s3n://emr.sagebase.org/output/debugLogs
And here is some sample output from the job. Note that:
User d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440is the platform@sagebase.org user.
arn:aws:iam::325565585839:user/prod-nicole.deflaux@sagebase.org [09/Aug/2011:01:07:49 +0000] REST.GET.OBJECT 4621/0.0.0/mouse_model_of_sexually_dimorphic_atherosclerotic_traits.phenotype.zip d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 [09/Aug/2011:01:48:49 +0000] REST.GET.BUCKET - d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 [09/Aug/2011:01:55:47 +0000] REST.GET.BUCKETPOLICY - d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 [09/Aug/2011:01:55:53 +0000] REST.GET.BUCKET - ... d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 [09/Aug/2011:01:56:30 +0000] REST.GET.ACL 5031/0.0.0/rClient/5030/sangerIC50.zip d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 [09/Aug/2011:01:56:30 +0000] REST.HEAD.OBJECT 5031/0.0.0/rClient/5030/sangerIC50.zip d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 [09/Aug/2011:01:56:30 +0000] REST.GET.OBJECT 5031/0.0.0/rClient/5030/sangerIC50.zip Downloads per file: - 14 5031/0.0.0/rClient/5030/sangerIC50.zip 3 4621/0.0.0/mouse_model_of_sexually_dimorphic_atherosclerotic_traits.phenotype.zip 1 Downloads per user: arn:aws:iam::325565585839:user/prod-nicole.deflaux@sagebase.org 1 d9df08ac799f2859d42a588b415111314cf66d0ffd072195f33b921db966b440 17 |
UPDATE: We no longer use bucket explorer to upload datasets. Instead we now use the R client to perform uploads. You can still use bucket explorer to browse datasets.
For the initial upload, a GUI tool called BucketExplorer (http://www.bucketexplorer.com/) is used. Uploads are done from the internal host sodo.fhcrc.org using the local access account 'platform', with the same password as the platform@sagebase.org account. The most efficient way to connect is to use an NX protocol client (http://www.nomachine.com/download.php) to get a virtual desktop as the user platform. Once connected the preconfigured BucketExplorer can be found in the application menu in the lower left corner of the screen.
Mac OSX Users I installed "NX Client for Mac OSX" but it complained that I was missing bin/nxssh and bin/nxservice. That stuff was not installed under Applications but instead under /Users/deflaux/usr/NX/
The initial datasets are stored in /work/platform/source/. This entire collection is mirrored exactly and can transfered by dragging and dropping into the data01.sagebase.org s3 bucket. This operation should be done as user platform, as all files should be readable by said user to facilitate the transfer. When adding a new dataset to /work/platform/source/, the script /work/platform/breakout_layers should be run as the platform user in order to breakout the layers into separate files. The script requires two arguments, one being the name of the dataset and two being the directory name in the source file that contains the dataset.
BucketExplorer is very efficient, and will do hash comparisons and only transfer what files have changed. One can also get a visual comparison of what files have changed using the 'Comparer' button. During the transfer, the program will parallelize the transfer into 20 streams for very efficient use of outgoing bandwidth to the cloud.
The policy below gives someone full access (list, read, write, delete) to your bucket.
{
"Id": "Policy1305325502034",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1305324625148",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::THE_BUCKET/*",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"THE_PERSONS_AWS_ACCOUNT_NUMBER"
]
}
},
{
"Sid": "Stmt1305325498087",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::THE_BUCKET",
"Principal": {
"AWS": [
"THE_PERSONS_AWS_ACCOUNT_NUMBER"
]
}
}
]
}
|
Use the MySQL client. You can install it locally on your machine (do this by installing a local MySQL database too.) Or you can use it on sodo.
The firewall currently only allows you to connect from a server inside the Fred Hutch network. If you are working from home, ssh to sodo and then do this. You can find the database password in sodo:/work/platform/PasswordsAndCredentials/passwords.txt
The produser account has full access to all databases, so be careful! The platform user is superuser and should only be used for creating new databases and users, and setting permissions.
~>hostname sodo ~>/usr/bin/mysql --ssl-ca=/work/platform/PasswordsAndCredentials/SshKeys/mysql-ssl-ca-cert.pem -u produser -h repo.c5sxx7pot9i8.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 6212 Server version: 5.5.8-log Source distribution Copyright (c) 2000, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This software comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. This is free software, and you are welcome to modify and redistribute it under the GPL v2 license Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | innodb | | performance_schema | | repositorydb | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.07 sec) mysql> use repositorydb; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A showDatabase changed mysql> show tables; +------------------------+ | Tables_in_repositorydb | +------------------------+ | JDOANALYSISRESULT | | JDOANNOTATIONS | | JDODATASET | | JDODATASETANALYSIS | | JDODATEANNOTATION | | JDODOUBLEANNOTATION | | JDOINPUTDATALAYER | | JDOLAYERLOCATION | | JDOLAYERLOCATIONS | | JDOLONGANNOTATION | | JDOPROJECT | | JDORESOURCEACCESS | | JDOREVISION | | JDOSCRIPT | | JDOSTRINGANNOTATION | | JDOUSER | | JDOUSERGROUP | | NUCLEUS_TABLES | +------------------------+ 18 rows in set (0.08 sec) mysql> desc JDODATASET; +---------------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | ID | bigint(20) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | ANNOTATIONS_ID_OID | bigint(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | | | CREATION_DATE | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | CREATOR | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | | | DESCRIPTION | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | | | NAME | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | | | NEXT_VERSION_ID_OID | bigint(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | | | RELEASE_DATE | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | REVISION_ID_OID | bigint(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | | | STATUS | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | | +---------------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 10 rows in set (0.07 sec) mysql> select count(*) from JDODATASET ; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 114 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.08 sec) mysql> quit |
Create your empty database
~/>/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -u root Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 1910 Server version: 5.5.9 MySQL Community Server (GPL) Copyright (c) 2000, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.06 sec) mysql> create database test2; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | test | | test2 | +--------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.04 sec) |
Note that the repository service will create the schema upon startup if it does not already exist.
Pass a property with your jdbc connection string:
-DJDBC_CONNECTION_STRING=jdbc:mysql://localhost/test2 |
The default username is 'root'. If you want a different username, pass it via property -DPARAM1=myUsername
The default password is the empty string. If you want a different password, pass it via property -DPARAM2=myUsername
The relevant code is in trunk/lib/jdomodels/src/main/java/org/sagebionetworks/repo/model/jdo/PMF.java.
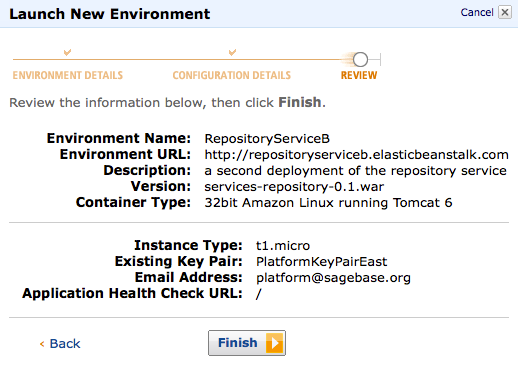
If you look at the running EC2 instances you will see a bunch of running EC2 instances in the elastic-beanstalk security group without names. To find the name, go to the running Beanstalk environment and click on logs -> snapshot logs to get the console to tell you the name of the underlying instance name: 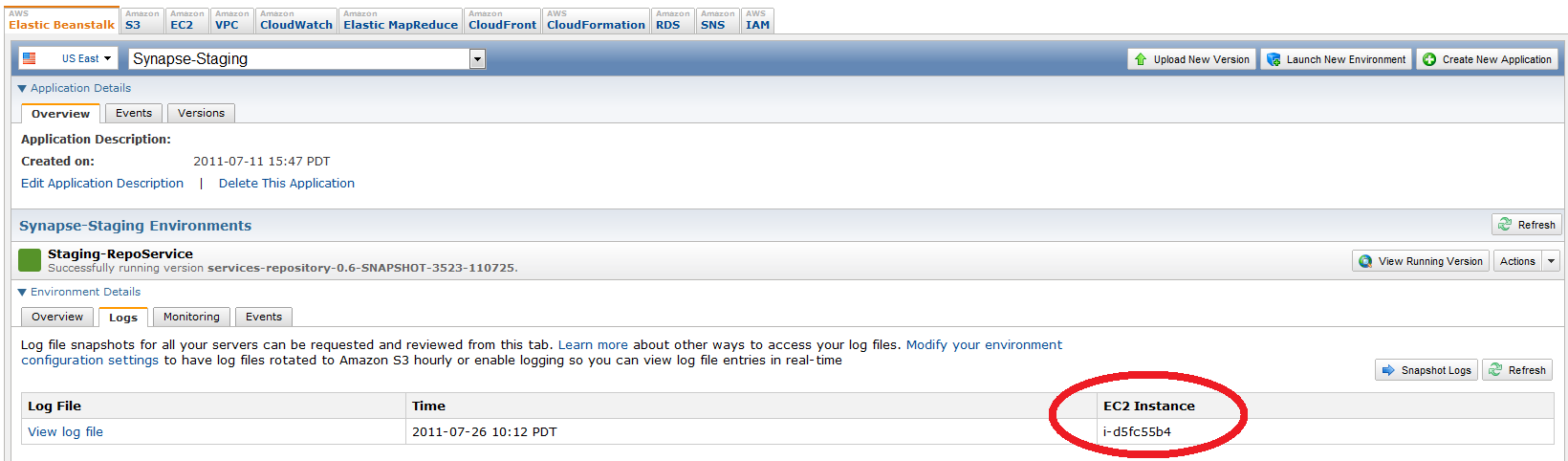
From this point, you can then go to the list of running EC2 instances and find your particular instance using the browser's find function. Note that you can rename the instances to match the beanstalk environment name, but that beanstalk recycles instances and will eventually replace your named instanced with a new one.
Once you have found the underlying instance, you can find the public DNS of that instance as a property of that instance. 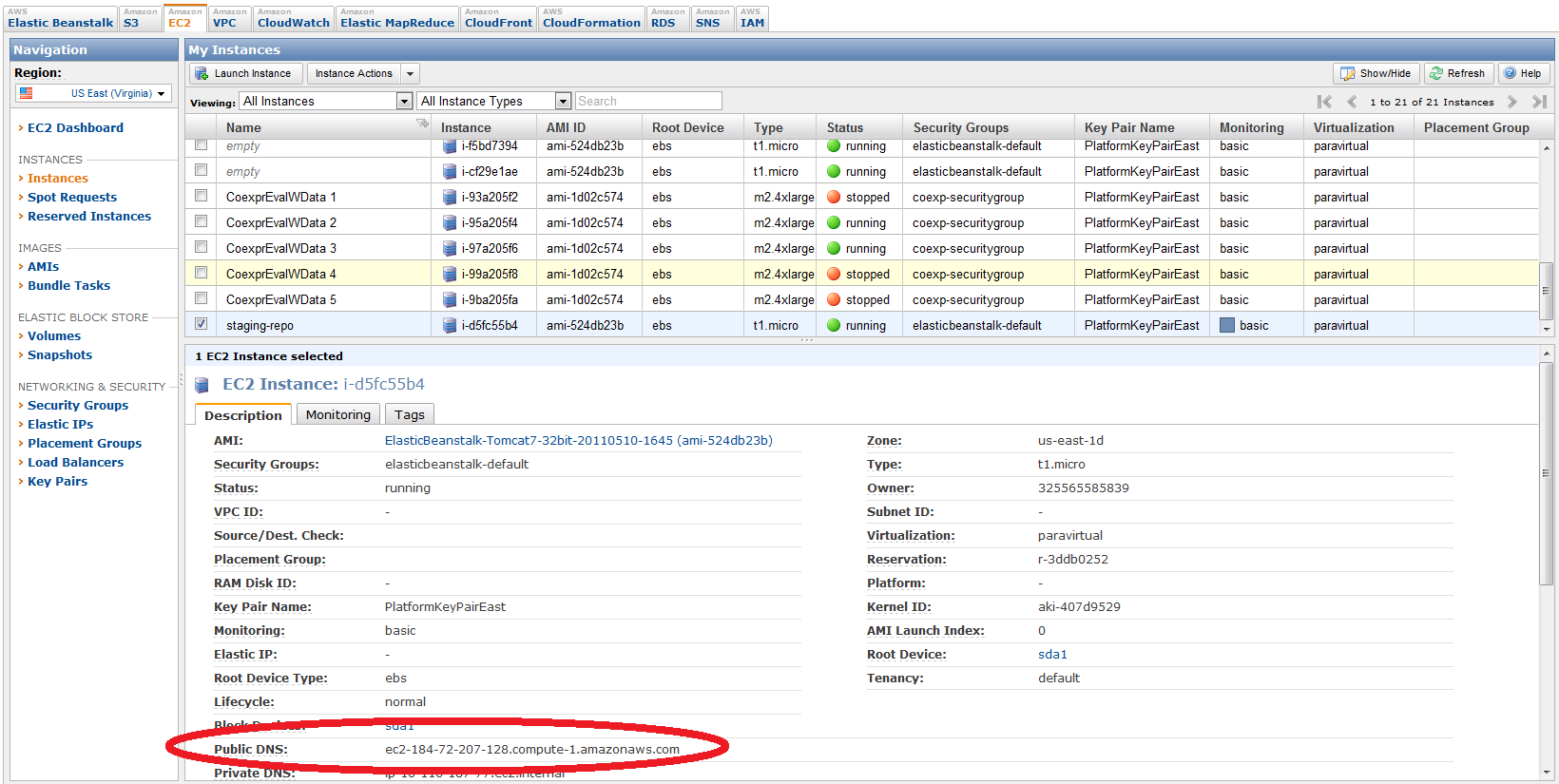
You can log on to the instance using this host name, the user "ec2-user" and a private key file generated for the private key file generated for the key pair. These are stored on sodo in /platform/work/PasswordsAndCredentials/SshKeys.
The servlet WAR is expanded under:
/opt/tomcat7/webapps/ROOT/var/lib/tomcat6/webapps/ROOT/If you want to save time (and a beanstalk deployment) you can overwrite that WAR with a new WAR if you want. Don't do this on the production stack though, only test stacks!
The tomcat 7 log files are here:
ls /opt/tomcat7/logs/ localhost_access_log.2011-06-13.txt catalina.out juli.2011-06-13.log monitor_catalina.log tail_catalina.log monitor_catalina.log.lck tail_catalina.log.lck |
The tomcat 6 log files are here:
/var/log /var/log/tomcat6/monitor_catalina.log.lck /var/log/tomcat6/tail_catalina.log /var/log/tomcat6/tail_catalina.log.lck /var/log/tomcat6/monitor_catalina.log |
The log files are here:
/var/log/httpd/error_log /var/log/httpd/access_log /var/log/httpd/elasticbeanstalk-access_log /var/log/httpd/elasticbeanstalk-error_log |
The ARN for the synapse.sagebase.org cert is arn:aws:iam::325565585839:server-certificate/SynapseCert
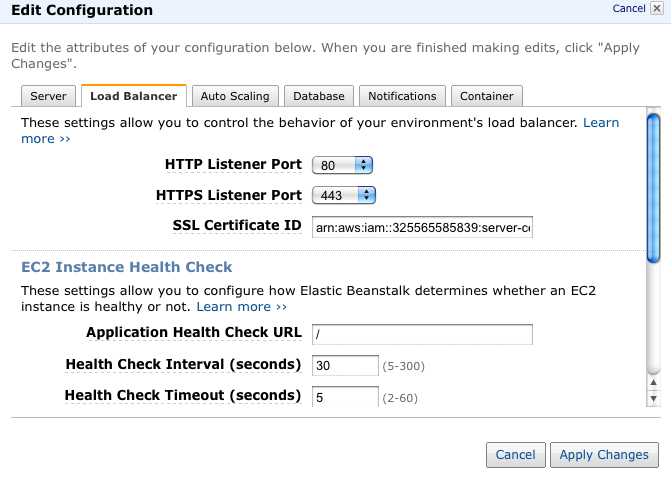
For links to more documentation and info about the ssl cert see PLFM-142
Here are some gotchas I ran into when using beanstalk for the first time:
In a tomcat container, such as Elastic Beanstalk, you have to include jstl.jar manually, hence this entry.
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
|