| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
See also: Bruce Hoff's presentation on his preliminary research into OAuth2 and how it relates to Synapse.
More reading for historical purposes: Synapse as OAuth 2.0 Provider
...
- Authorization Code grant (most secure, client secret confidentiality must be guaranteed)
- Upon user consent, an OAuth client (3rd party) is granted an authorization code
- The authorization code can be used with a client secret to obtain a scoped access token.
- The access token can be used to access resources until it expires or is revoked
- The access token can be refreshed by the client with a refresh token and the client secret.
- Implicit code grant (client secret confidentiality cannot be guaranteed)
- Upon user consent, an OAuth client (3rd party) is granted a scoped access token.
- The token can be used to access resources until it is expired or revoked, but it cannot be refreshed. The time that the token is active is typically very short (minutes).
- Resource owner password credentials (not secure, especially with an untrusted client)
- The user provides their username and password to the OAuth client
- The OAuth client uses the credentials to obtain a scoped access token
- Client credentials (used for cases where clients manage their own resources, i.e. not really authorization delegation)
- The OAuth client can request an access token with their client ID and client secret
OAuth2 in Synapse - API Design
The current proposal is to introduce OAuth2 authorization code and implicit code flows flow into Synapse. OAuth clients would be instructed to use authorization codes only. Implicit grant type may only be used by an internal, bootstrapped Synapse OAuth client to issue scoped session tokens.
Backend
We can separate the endpoints required on the backend based on task.
...
| Verb | Endpoint | Purpose | Request | Response | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
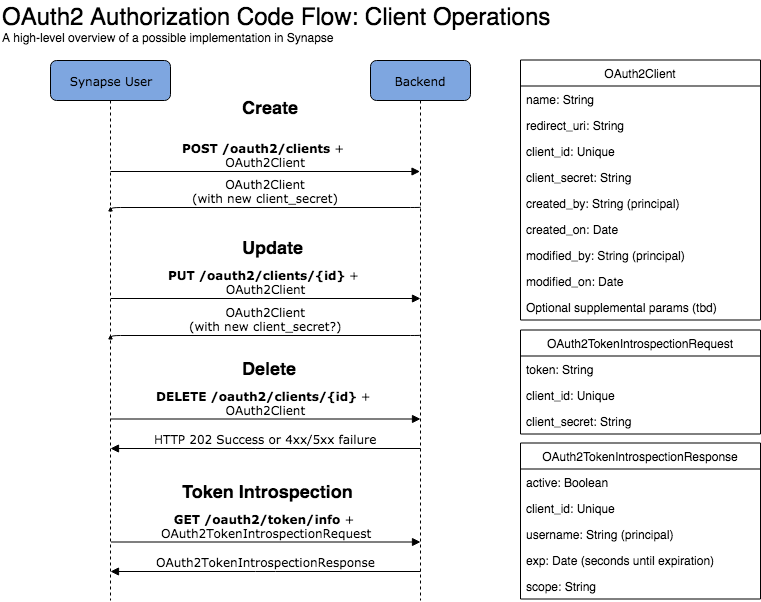
| GET | /oauth2/clientsclient/{id} | Get details about one client | Path param: id: an existing OAuth2 Client ID | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String client_id: Unique created_by/on modified_by/on Supplemental params | Necessary? May not need thisOnly the owner or a Synapse admin can make this request. | |
| GET | /oauth2/client/ | List clients created by user | List of above. | Don't return secret. | ||
| POST | /oauth2/clientsclient | Create a client | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String Supplemental params | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String created_by/on modified_by/on | Supplemental params | Supplemental params could include the URL to a logo, link to a website for the app, terms of service, etc. See https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-registration-1_0.html Typically the secret key is used to perform these actions, but if we give Synapse users a claim over an OAuth2 client, we could use their credentials. |
| DELETE | /oauth2/clientsclient/{id} | Delete a client | Path param: id: an existing OAuth2 Client ID | None | ||
| PUT | /oauth2/clientsclient/{id} | Update a client | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String Supplemental params | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String client_id: Unique created_by/on modified_by/on Supplemental params | Typically the secret key is used to perform these actions, but if we give Synapse users a claim over an OAuth2 client, we could use their credentials. |
...
| Verb | Endpoint | Purpose | Request Object/Params | Response Object/Params | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POST | /login/scoped | Get a scoped access token | sessionToken: String scope: String | scopedLoginResponse: scopedSessionToken: String acceptsTermsOfUse: Boolean scope: String exp: Integer (seconds until expiry) | This is a more secure alternative to the current session token as limits what can be done with the session token. These can (should?) expire quickly (minutes-hours). This could be done by passing in username and password rather than sessionToken, but we'd have to handle the case where the user has no password and logs in via Google (or other OAuth provider). |
| GET | /oauth2/details | Get human-interpretable details about the requesting client, and the scope that they are requesting | Parameters clientId: Unique (the ID of an existing OAuth2 client requesting access) scope: String | OAuth2Client scopes: Array<string> e.g. [("read", "syn123"), ("create","syn456")] (actual representation TBD) | The web layer can use this to get details about a client requesting authorization and the scope they request |
| POST | /oauth2/consent | The user grants access to the OAuth2 Client to access protected resources | URL Parameters: response_type: String (always "code") client_id: Unique redirect_uri: String (points to OAuth client) scope: String state: String | If login is successfulscopedAccessToken is valid: Body: Redirect URLOAuthClientUrl: String redirect_uri?code={code}&state={state} (all provided in request) Parameters: code: the authorization code state: the same value in the request | Who should execute this? The User Agent or the Web Layer on behalf of the user agent? Question: how to handle with various Synapse IdPs? (E.g. Synapse users who sign in with Google accounts). The "state" parameter is designed to avoid CSRF attacks and the client must utilize it per RFC-6749 § 10.12. More info. |
| OAuth2RevokeRequestO
|
|
Token Requests
These endpoints would be used by OAuth2.0 clients to retrieve tokens with an access code
| Verb | Endpoint | Purpose | Request | Response | Notes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POST | /oauth2/token | Called by a client to get an access token | Body: OAuth2AuthorizationCodeTokenRequest grant_type: String (always "authorization_code" for this call) code: String (the authorization code) redirect_uri: String (should be the same as previous redirect uri) client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2AccessToken access_token: String token_type: String ("Bearer") expires_in: Integer (seconds) refresh_token: String (optionally, scope) | The redirect URI should be validated here before granting a token, along with the credentials in the request. More info. The token type in almost all OAuth2 cases is "Bearer". We can use a different token type (e.g. HMAC, or make our own) if we want to, but there is probably no need. More info. | POST | /oauth2/token/refresh | Called by a client to refresh an access token | Body: OAuth2AuthorizationCodeRefreshTokenRequest grant_type: String (always "refresh_token" for this call) refresh_token: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2AccessToken access_token: String token_type: String ("Bearer") expires_in: Integer (seconds) refresh_token: String |
| GET | /oauth2/token/introspect or /oauth2/token/info | Clients can determine if an authentication token is valid (and get scope, if it is opaque in the token) | Body: OAuth2TokenIntrospectionRequest token: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2TokenIntrospectionResponse active: Boolean client_id: Unique username: String (principal of user who authorized) exp: Date (seconds until expiration) scope: Array<String> (human-interpretable scope) | This endpoint is not strictly necessary, but we should strongly consider including this if we decide to not include scope with the access token |
Web Layer Interfaces (Portal)
The portal needs to implement interfaces for handling the components of OAuth2 that are best accomplished through user interfaces.
...
Prompt for authentication (u:p/OAuth login)
Retrieve a scoped access token on behalf of the user (which can only be used to authorize OAuth2 authorization requests)
Redirect to/render OAuth2.0 Authorization Request
...
Retrieve/interpret client details + scope and display to the user "Do you want Client123 to have full access over syn123"
Approve/reject OAuth2 request on behalf of the user
Redirect user-agent to OAuth2AuthorizedUrl (provided by backend)
Diagrams to show where these API endpoints would be used and what objects/params are needed:
How do we know if we're up-to-spec when we are done?
If we implement OIDC, there is a process to become OIDC-certified here: https://openid.net/certification/
I think that to have OIDC configured properly, you must have OAuth2 configured properly, so this would cover both cases. (I would like to investigate this further if we do decide to implement OIDC)
If we do not implement OIDC (just OAuth2) there doesn't seem to be any certification process that I can find. We may have to read the spec ourselves and hope we don't miss anything with thorough tests, future security audits, etc.
What is "scope"?
JIRAs(?):
| Jira Legacy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In short: scopes are clearly defined permissions that a user may grant to an OAuth client.
In ORY Hydra, OAuth clients may be limited in the scope they can request (e.g. a photo printing service (OAuth client) may be restricted to only acquire read-photo permission, even if they attempt to request edit-photo permission). This is not a requirement of our implementation, but it is worth consideration.
From RFC-6749
...
As per OIDC the response should include both an access token and an ID Token, https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#TokenResponse Authorization codes must be single-use and short-lived. If an authorization code is used more than once, we should revoke the active access token retrieved with the code. More info @ RFC-6749 § 10.5 The redirect URI should be validated here before granting a token, along with the credentials in the request. More info @ RFC-6749 § 10.6. The token should be opaque/unguessable. More info @ RFC-6749 § 10.3. Update: token could be JWT, https://www.oauth.com/oauth2-servers/access-tokens/self-encoded-access-tokens/. Advantage is that permissions are 'built in' to the token. Downside is that it becomes irrevocable. So let's not use JWT. The token type in almost all OAuth2 cases is "Bearer". We can use a different token type (e.g. HMAC, or make our own) if we want to. See RFC-6749 § 7.1. Additional info. | |||||
| POST | /oauth2/token/refresh | Called by a client to refresh an access token | Body: OAuth2AuthorizationCodeRefreshTokenRequest grant_type: String (always "refresh_token" for this call) refresh_token: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2AccessToken access_token: String token_type: String ("Bearer") expires_in: Integer (seconds) refresh_token: String | Client authentication must be done here. This must be done over TLS. More info @ RFC-6749 § 10.4 |
| POST | /oauth2/token/introspect or /oauth2/token/info | Clients can determine if an authentication token is valid (and get scope, if it is opaque in the token) | Body: OAuth2TokenIntrospectionRequest token: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2TokenIntrospectionResponse active: Boolean client_id: Unique username: String (principal of user who authorized the token) exp: Date (seconds until expiration) scope: Array<String> (human-interpretable scope) | This endpoint is not strictly necessary, but we should strongly consider including this if we decide to not include scope with the access token. See RFC-7662. |
OpenID Connect services
| Verb | Endpoint | Purpose | Request | Response | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /.well-known/openid-configuration | return metadata about the service | N/A | See spec -→ Key elements are:
| https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfigurationRespon |
| GET | /oauth2/userinfo | return information about the user | N/A | Body: sub: "subject", Synapse user id aud: "audience", the OAuth client ID iat: "issued at", the timestamp when the response was created given_name: first name family_name: last name | https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#UserInfo Note: content type must be application/jwt as per https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#UserInfoResponse |
| POST | /oauth2/userinfo | as above | N/A | as above | Although GET is the recommended HTTP method, POST must be supported, as per https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#UserInfo |
Web Layer Interfaces (Portal)
The portal needs to implement interfaces for handling the components of OAuth2 that are best accomplished through user interfaces.
| Page | Purpose | Actions |
|---|---|---|
| OAuth2 Authentication | Provides an interface for the user to authenticate in order to manage OAuth2 requests | Prompt for authentication (u:p/OAuth login) Retrieve a scoped access token on behalf of the user (which can only be used to authorize OAuth2 authorization requests) Redirect to/render OAuth2.0 Authorization Request |
| OAuth2 Authorization | Provides an interface for the user to approve/reject OAuth requests | Retrieve/interpret client details + scope and display to the user "Do you want Client123 to have full access over syn123" Approve/reject OAuth2 request on behalf of the user Redirect user-agent to OAuth2AuthorizedUrl (provided by backend) |
Diagrams to show where these API endpoints would be used and what objects/params are needed:
How do we know if we're up-to-spec when we are done?
If we implement OIDC, there is a process to become OIDC-certified here: https://openid.net/certification/
I think that to have OIDC configured properly, you must have OAuth2 configured properly, so this would cover both cases. (I would like to investigate this further if we do decide to implement OIDC)
If we do not implement OIDC (just OAuth2) there doesn't seem to be any certification process that I can find. We may have to read the spec ourselves and hope we don't miss anything with thorough tests, future security audits, etc.
What is "scope"?
JIRA:
| Jira Legacy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In short: scopes are clearly defined permissions that a user may grant to an OAuth client.
In ORY Hydra, OAuth clients may be limited in the scope they can request (e.g. a photo printing service (OAuth client) may be restricted to only acquire read-photo permission, even if they attempt to request edit-photo permission). This is not a requirement of our implementation, but it is worth consideration.
From RFC-6749
The authorization and token endpoints allow the client to specify the scope of the access request using the "scope" request parameter. In turn, the authorization server uses the "scope" response parameter to inform the client of the scope of the access token issued.
The value of the scope parameter is expressed as a list of space-delimited, case-sensitive strings. The strings are defined by the authorization server. If the value contains multiple space-delimited strings, their order does not matter, and each string adds an additional access range to the requested scope. scope = scope-token *( SP scope-token ) scope-token = 1*( %x21 / %x23-5B / %x5D-7E )
The authorization server MAY fully or partially ignore the scope requested by the client, based on the authorization server policy or the resource owner's instructions. If the issued access token scope is different from the one requested by the client, the authorization server MUST include the "scope" response parameter to inform the client of the actual scope granted. If the client omits the scope parameter when requesting authorization, the authorization server MUST either process the request using a pre-defined default value or fail the request indicating an invalid scope. The authorization server SHOULD document its scope requirements and default value (if defined).
...
The administrative port should not be exposed to public internet traffic. If you want to expose certain endpoints, such as the
/clientsendpoint for OpenID Connect Dynamic Client Registry, you can do so but you need to properly secure these endpoints with an API Gateway or Authorization Proxy.
Do we need this?
Spring Security
...
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52683165/creating-oauth-2-0-login-provider-with-spring-boot
OIDC is a layer on top of OAuth, why can we not just implement it on top of the old version of Spring Security?
codetokenid_tokenid_token tokencode id_tokencode tokencode id_token tokennone
The old version of Spring Security was not built to handle this. Here is the issue (which has not been resolved at the time of writing: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-security-oauth/issues/619)
The answerer of the SO post also has a blog post that goes more in-depth: https://medium.com/@darutk/full-scratch-implementor-of-oauth-and-openid-connect-talks-about-findings-55015f36d1c3
So in theory you could develop something OIDC-like on top of the existing infrastructure, but it won't be spec-compliant, which is a considerable drawback for a service designed for external services that are not supported by Synapse engineers.
So how would we use Spring Security?
First we need to make sure it can handle all of our needs. Spring Security 5 development on OAuth2+OIDC support is incomplete (as of Oct 2018), so it isn't guaranteed that it can currently do what we need it to.
This features matrix shows the state of OAuth2 support in Spring Security 5 (and compares it to Spring Security OAuth 2, the old version). Note that this has not been updated since Jan 2018, and I suspect it is out of date.
Of note:
What is the future of OAuth 2.0 support in Spring Security?
The next generation of OAuth 2.0 support is currently underway in Spring Security 5, as we introduced new Client support for the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework and OpenID Connect Core 1.0. The plan is to also provide support for Resource Server by mid-2018 and Authorization Server by the end of 2018 or early 2019 along with more extensive support for OAuth 2.0 Core and Extensions, OpenID Connect 1.0 and Javascript Object Signing and Encryption (JOSE).
Are there new features being implemented in Spring Security OAuth 2.2+?
We will provide bug/security fixes and consider adding minor features but we will not be adding major features. Our plan going forward is to build all the features currently in Spring Security OAuth into Spring Security 5.x. After Spring Security has reached feature parity with Spring Security OAuth, we will continue to support bugs and security fixes for at least one year.
Here are some SpringBoot examples that we could consider looking at. They are built into the current version of Spring Security but they use the old Spring Security OAuth module.
The Spring Security 5.2 Docs only outline configuring an OAuth2 Resource Server, which simplifies validation of that tokens from an Authorization server. It's not immediately clear if that buys us anything, since we have to write our own Authorization and Token-issuing service anyways (the use cases they give involve using a federated authorization server, e.g. Okta).
The (old) Spring Security OAuth2 supports creating an OAuth2 Authorization server. If we decide we never need OIDC (or we are content with potentially having to rewrite this component later), then I believe this will work fine (assuming the module will receive maintenance for at least a few more years to come.
Can we use Spring Security to manage tokens?
Depends on which module we use (Security 5 vs OAuth module)
Spring Security 5
The OAuth2 Resource Server supports decoding JWT tokens. There is no token generation system implemented at the time of writing (Oct 2018)
Spring Security OAuth
To some extent:
When creating your
AuthorizationServerTokenServicesimplementation, you may want to consider using theDefaultTokenServiceswhich has many strategies that can be plugged in to change the format and storage of access tokens. By default it creates tokens via random value and handles everything except for the persistence of the tokens which it delegates to aTokenStore. The default store is an in-memory implementation, but there are some other implementations available. Here's a description with some discussion of each of them
The
JdbcTokenStoreis the JDBC version of the same thing, which stores token data in a relational database. Use the JDBC version if you can share a database between servers, either scaled up instances of the same server if there is only one, or the Authorization and Resources Servers if there are multiple components. To use theJdbcTokenStoreyou need "spring-jdbc" on the classpath.The JSON Web Token (JWT) version of the store encodes all the data about the grant into the token itself (so no back end store at all which is a significant advantage). One disadvantage is that you can't easily revoke an access token, so they normally are granted with short expiry and the revocation is handled at the refresh token. Another disadvantage is that the tokens can get quite large if you are storing a lot of user credential information in them. The
JwtTokenStoreis not really a "store" in the sense that it doesn't persist any data, but it plays the same role of translating betweeen token values and authentication information in theDefaultTokenServices.
There is no provided JDBC schema because it is designed to be configurable for the specific use case, but they have examples available.provider-with-spring-boot
How would we use Spring Security?
First we need to make sure it can handle all of our needs. Spring Security 5 development on OAuth2+OIDC support is incomplete (as of Oct 2018), so it isn't guaranteed that it can currently do what we need it to.
This features matrix shows the state of OAuth2 support in Spring Security 5 (and compares it to Spring Security OAuth 2, the old version). Note that this has not been updated since Jan 2018, and I suspect it is out of date.
Of note:
What is the future of OAuth 2.0 support in Spring Security?
The next generation of OAuth 2.0 support is currently underway in Spring Security 5, as we introduced new Client support for the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework and OpenID Connect Core 1.0. The plan is to also provide support for Resource Server by mid-2018 and Authorization Server by the end of 2018 or early 2019 along with more extensive support for OAuth 2.0 Core and Extensions, OpenID Connect 1.0 and Javascript Object Signing and Encryption (JOSE).
Are there new features being implemented in Spring Security OAuth 2.2+?
We will provide bug/security fixes and consider adding minor features but we will not be adding major features. Our plan going forward is to build all the features currently in Spring Security OAuth into Spring Security 5.x. After Spring Security has reached feature parity with Spring Security OAuth, we will continue to support bugs and security fixes for at least one year.
Here are some SpringBoot examples that we could consider looking at. They are built into the current version of Spring Security but they use the old Spring Security OAuth module.
The Spring Security 5.2 Docs only outline configuring an OAuth2 Resource Server, which simplifies validation of that tokens from an Authorization server. It's not immediately clear if that buys us anything, since we have to write our own Authorization and Token-issuing service anyways (the use cases they give involve using a federated authorization server, e.g. Okta).
The (old) Spring Security OAuth2 supports creating an OAuth2 Authorization server. If we decide we never need OIDC (or we are content with potentially having to rewrite this component later), then I believe this will work fine (assuming the module will receive maintenance for at least a few more years to come.
Can we use Spring Security to manage tokens?
Depends on which module we use (Security 5 vs OAuth module)
Spring Security 5
The OAuth2 Resource Server supports decoding JWT tokens. There is no token generation system implemented at the time of writing (Oct 2018)
Spring Security OAuth
To some extent:
When creating your
AuthorizationServerTokenServicesimplementation, you may want to consider using theDefaultTokenServiceswhich has many strategies that can be plugged in to change the format and storage of access tokens. By default it creates tokens via random value and handles everything except for the persistence of the tokens which it delegates to aTokenStore. The default store is an in-memory implementation, but there are some other implementations available. Here's a description with some discussion of each of them
The
JdbcTokenStoreis the JDBC version of the same thing, which stores token data in a relational database. Use the JDBC version if you can share a database between servers, either scaled up instances of the same server if there is only one, or the Authorization and Resources Servers if there are multiple components. To use theJdbcTokenStoreyou need "spring-jdbc" on the classpath.The JSON Web Token (JWT) version of the store encodes all the data about the grant into the token itself (so no back end store at all which is a significant advantage). One disadvantage is that you can't easily revoke an access token, so they normally are granted with short expiry and the revocation is handled at the refresh token. Another disadvantage is that the tokens can get quite large if you are storing a lot of user credential information in them. The
JwtTokenStoreis not really a "store" in the sense that it doesn't persist any data, but it plays the same role of translating betweeen token values and authentication information in theDefaultTokenServices.
There is no provided JDBC schema because it is designed to be configurable for the specific use case, but they have examples available.
Why using the Spring Security OAuth Module prevents us from extending our OAuth implementation to include OIDC
codetokenid_tokenid_token tokencode id_tokencode tokencode id_token tokennone
The old version of Spring Security was not built to handle this. Here is the issue (which has not been resolved at the time of writing: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-security-oauth/issues/619)
The answerer of the SO post also has a blog post that goes more in-depth: https://medium.com/@darutk/full-scratch-implementor-of-oauth-and-openid-connect-talks-about-findings-55015f36d1c3
So in theory you could develop something OIDC-like on top of the existing infrastructure, but it won't be spec-compliant, which is a considerable drawback for a service designed for external services that are not supported by Synapse engineers.
Another library to look into: Connect2ID's OAuth2.0 SDK with OpenID Connect
Spring Security OAuth actually uses this internally
...

.png?version=1&modificationDate=1564589737737&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)