This page is starting as a collection of notes, design decisions, etc. related to implementing OAuth2 into Synapse. Part of the process has included considerations about developing our own library, or using an off-the-shelf solution like ORY Hydra. The information on this page may change as the project evolves.
See also: Bruce Hoff's presentation on his preliminary research into OAuth2 and how it relates to Synapse.
More reading: Synapse as OAuth 2.0 Provider
And a Jira Epic:
| Jira Legacy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Good summary of OIDC: https://github.com/dexidp/dex/blob/master/Documentation/openid-connect.md
Use cases
High level use-cases, per Bruce Hoff's presentation:
- Let third party (web) app’s securely access a user’s data in Synapse. Today such app’s must either
- predownload/embed data,
- use the app’ author’s Synapse credentials, or
- prompt the user for their Synapse credentials
- Let a headless batch job (e.g.,a “workflow”) securely access a user’s data in Synapse. Today such a process must either
- Use predownloaded data
- Use the job runner’s Synapse credentials
These use cases must guide how we encode scope.
Some questions:
- How granular do we expect scope must be?
- Do Read/Edit/Write permissions cover all use cases?
- Do permissions need to be set on the entity level?
- e.g. can we afford to make all cases "this external app can read everything you have access to" vs
- this external app can read "syn123, a file in project syn999"
Basic OAuth or OAuth-like flow (authorization grant only, no external tools)
To implement the bare minimum to address use cases with an OAuth-like flow, we need
- Endpoints to create, read, list, delete (and optionally, update) clients
- Authentication code generation
...
Get a list of all clients
...
Client API access can be restricted based on our needs.
- All registered Synapse users?
- Approved OAuth API users?
- OAuth Administrators?
...
what information do we need from a client?
client object
...
client object + secret key (do not store the secret key)
...
Prompt user for request when they call this.
Show as much relevant information as possible (X app wants Y permission on Z resource)
...
client (ID)
request_url (String)
requested_scope (array of string)
...
Web interface for Synapse authorization
...
client (ID)
request_url (String)
requested_scope (array of string)
LoginRequest
...
Redirect URL containing authentication code tied to the input client ID and the scope
LoginResponse?
...
authentication token
refresh token
...
Diagram from the above presentation, edited to show where these API endpoints would be used:
Database models: what do we need to store?
TBDThis page is starting as a collection of notes, design decisions, etc. related to implementing OAuth2 into Synapse. Part of the process has included considerations about developing our own library, or using an off-the-shelf solution like ORY Hydra. The information on this page may change as the project evolves.
See also: Bruce Hoff's presentation on his preliminary research into OAuth2 and how it relates to Synapse.
More reading: Synapse as OAuth 2.0 Provider
And a Jira Epic:
| Jira Legacy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Good summary of OIDC: https://github.com/dexidp/dex/blob/master/Documentation/openid-connect.md
Use cases
High level use-cases, per Bruce Hoff's presentation:
- Let third party (web) app’s securely access a user’s data in Synapse. Today such app’s must either
- predownload/embed data,
- use the app’ author’s Synapse credentials, or
- prompt the user for their Synapse credentials
- Let a headless batch job (e.g.,a “workflow”) securely access a user’s data in Synapse. Today such a process must either
- Use predownloaded data
- Use the job runner’s Synapse credentials
These use cases must guide how we encode scope.
Some questions:
- How granular do we expect scope must be?
- Do Read/Edit/Write permissions cover all use cases?
- Do permissions need to be set on the entity level?
- e.g. can we afford to make all cases "this external app can read everything you have access to" vs
- this external app can read "syn123, a file in project syn999"
Basic OAuth or OAuth-like flow (authorization code flow only, with no external tools)
To implement the bare minimum to address use cases with an OAuth-like flow, we need
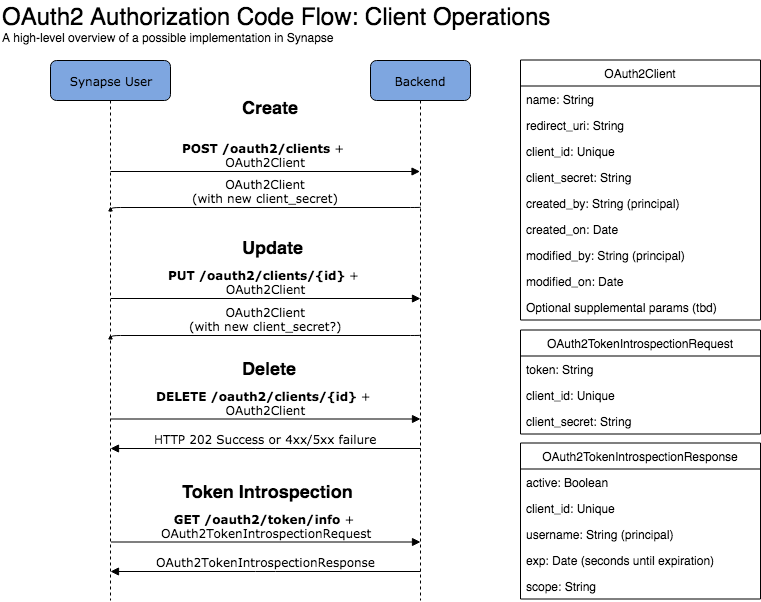
- Endpoints to create, read, list, delete (and optionally, update) clients
- Authentication code generation
| Verb | Endpoint | Purpose | Request Object/Params | Response Object/Params | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /oauth2/clients/{id} | Get details about one client | Path param: id: an existing OAuth2 Client ID | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String client_id: Unique created_by/on modified_by/on Supplemental params | The web layer can use this to get details about a client requesting authorization. |
| POST | /oauth2/clients | Create a client | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String Supplemental params | OAuth2Client name: String redirect_uri: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String created_by/on modified_by/on Supplemental params | Supplemental params could include the URL to a logo, link to a website for the app, terms of service, etc. Typically the secret key is used to perform these actions, but if we give Synapse users a claim over an OAuth2 client, we could use their credentials. |
| DELETE | /oauth2/clients/{id} | Delete a client | Path param: id: an existing OAuth2 Client ID | None | |
| GET | /oauth2/auth | Display the login/consent info to the user and prompt for an accept/reject | URL Parameters: response_type: String (always "code") client_id: Unique redirect_uri: String (points to OAuth client) scope: String state: String | Web interface for Synapse authorization The form should permit login and we must be able to include the request parameters in a new request | This endpoint should point to a web layer that can show a UI with a login form and display the access that the user can consent to, along with a prompt for the user to accept/reject. We should think about using login cookies here to simplify the UX if a user is already logged into Synapse |
| POST | /oauth2/auth | The user grants access to the OAuth2 Client to access protected resources | URL Parameters: response_type: String (always "code") client_id: Unique redirect_uri: String (points to OAuth client) scope: String state: String Body: LoginRequest (already exists) | If login is successful: Redirect URL: redirect_uri (provided in request) Parameters: code: the authorization code state: the same value in the request Should we include a LoginResponse body? (Probably not, if the body is kept in the redirect then we may be exposing a session token to the 3rd party client) | Who should execute this? The User Agent or the Web Layer on behalf of the user agent? Question: how to handle with various Synapse IdPs? (E.g. Synapse users who sign in with Google accounts). The "state" parameter is designed to avoid CSRF attacks. More info. |
| POST | /oauth2/token | Called by a client to get an access token | Body: OAuth2AuthorizationCodeTokenRequest grant_type: String (always "authorization_code" for this call) code: String (the authorization code) redirect_uri: String (should be the same as previous redirect uri) client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2AccessToken access_token: String token_type: String ("Bearer") expires_in: Integer (seconds) refresh_token: String (optionally, scope) | The redirect URI should be validated here before granting a token, along with the credentials in the request. More info. The token type in almost all OAuth2 cases is "Bearer". We can use a different token type (or make our own) if we want to, but there is probably no need. More info. |
| POST | /oauth2/token or /oauth2/token/refresh | Called by a client to refresh an authentication token | Body: OAuth2AuthorizationCodeRefreshTokenRequest grant_type: String (always "refresh_token" for this call) refresh_token: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2AccessToken access_token: String token_type: String ("Bearer") expires_in: Integer (seconds) refresh_token: String | |
| GET | /oauth2/token/introspect or /oauth2/token/info | Clients can determine if an authentication token is valid (and get scope, if it is opaque in the token) | Body: OAuth2TokenIntrospectionRequest token: String client_id: Unique client_secret: String | Body: OAuth2TokenIntrospectionResponse active: Boolean client_id: Unique username: String (principal of user who authorized) exp: Date (seconds until expiration) scope: String | We must have this if we decide to not include scope with the access token |
| POST | /oauth2/revoke | A logged in user can revoke OAuth2 client access using this method. | OAuth2RevokeRequest client_id: unique Is there a need for more granularity? | None | Revoking access not in the OAuth2 spec but allowing users to revoke client access may be important. |
Diagrams to show where these API endpoints would be used and what objects/params are needed:
What is "scope"?
...
The administrative port should not be exposed to public internet traffic. If you want to expose certain endpoints, such as the
/clientsendpoint for OpenID Connect Dynamic Client Registry, you can do so but you need to properly secure these endpoints with an API Gateway or Authorization Proxy.
Do we need this?
Spring Security
...